pacman::p_load(tidyverse, FunnelPlotR, plotly, knitr) Hands-on Exercise 4d:Funnel Plots for Fair Comparisons
1 Getting Started
In this exercise, we will use the following our R packages.
readr for importing csv into R.
FunnelPlotR for creating funnel plot.
ggplot2 for creating funnel plot manually.
knitr for building static html table.
plotly for creating interactive funnel plot.
The code chunk below uses p_load() of pacman package to check if these packages are installed in the computer and load them onto your working R environment.
The code chunk below imports exam_data.csv into R environment by using read_csv() function of readr package.
covid19 <- read_csv("data/COVID-19_DKI_Jakarta.csv") %>%
mutate_if(is.character, as.factor)The code chunk below uses summary()to summarize the data.
summary(covid19) Sub-district ID City District
Min. :3.101e+09 JAKARTA BARAT :56 TAMBORA : 11
1st Qu.:3.172e+09 JAKARTA PUSAT :44 KEBAYORAN BARU: 10
Median :3.173e+09 JAKARTA SELATAN :65 CIPAYUNG : 8
Mean :3.172e+09 JAKARTA TIMUR :65 JATINEGARA : 8
3rd Qu.:3.174e+09 JAKARTA UTARA :31 KEMAYORAN : 8
Max. :3.175e+09 KAB.ADM.KEP.SERIBU: 6 SETIA BUDI : 8
(Other) :214
Sub-district Positive Recovered Death
ANCOL : 1 Min. : 72 Min. : 69 Min. : 0.00
ANGKE : 1 1st Qu.:1644 1st Qu.:1578 1st Qu.: 24.50
BALE KAMBANG: 1 Median :2420 Median :2329 Median : 39.00
BALI MESTER : 1 Mean :2572 Mean :2477 Mean : 40.99
BAMBU APUS : 1 3rd Qu.:3372 3rd Qu.:3242 3rd Qu.: 55.00
BANGKA : 1 Max. :6231 Max. :5970 Max. :158.00
(Other) :261 2 FunnelPlotR methods
FunnelPlotR package uses ggplot to generate funnel plots. It requires a numerator (events of interest), denominator (population to be considered) and group. The key arguments selected for customisation are:
limit: plot limits (95 or 99).label_outliers: to label outliers (true or false).Poisson_limits: to add Poisson limits to the plot.OD_adjust: to add overdispersed limits to the plot.xrangeandyrange: to specify the range to display for axes, acts like a zoom function.Other aesthetic components such as graph title, axis labels etc.
2.1 FunnelPlotR methods: The basic plot
The code chunk below plots a funnel plot.
funnel_plot(numerator = covid19$Positive,
denominator = covid19$Death,
group = covid19$`Sub-district`)
A funnel plot object with 267 points of which 0 are outliers.
Plot is adjusted for overdispersion. groupin this function is different from the scatterplot. Here, it defines the level of the points to be plotted i.e. Sub-district, District or City. If Cityc is chosen, there are only six data points.By default,
data_typeargument is “SR”.limit: Plot limits, accepted values are: 95 or 99, corresponding to 95% or 99.8% quantiles of the distribution.
2.2 Makeover 1
The code chunk below plots a funnel plot.
funnel_plot(
numerator = covid19$Death,
denominator = covid19$Positive,
group = covid19$`Sub-district`,
data_type = "PR", #<<
xrange = c(0, 6500), #<<
yrange = c(0, 0.05) #<<
)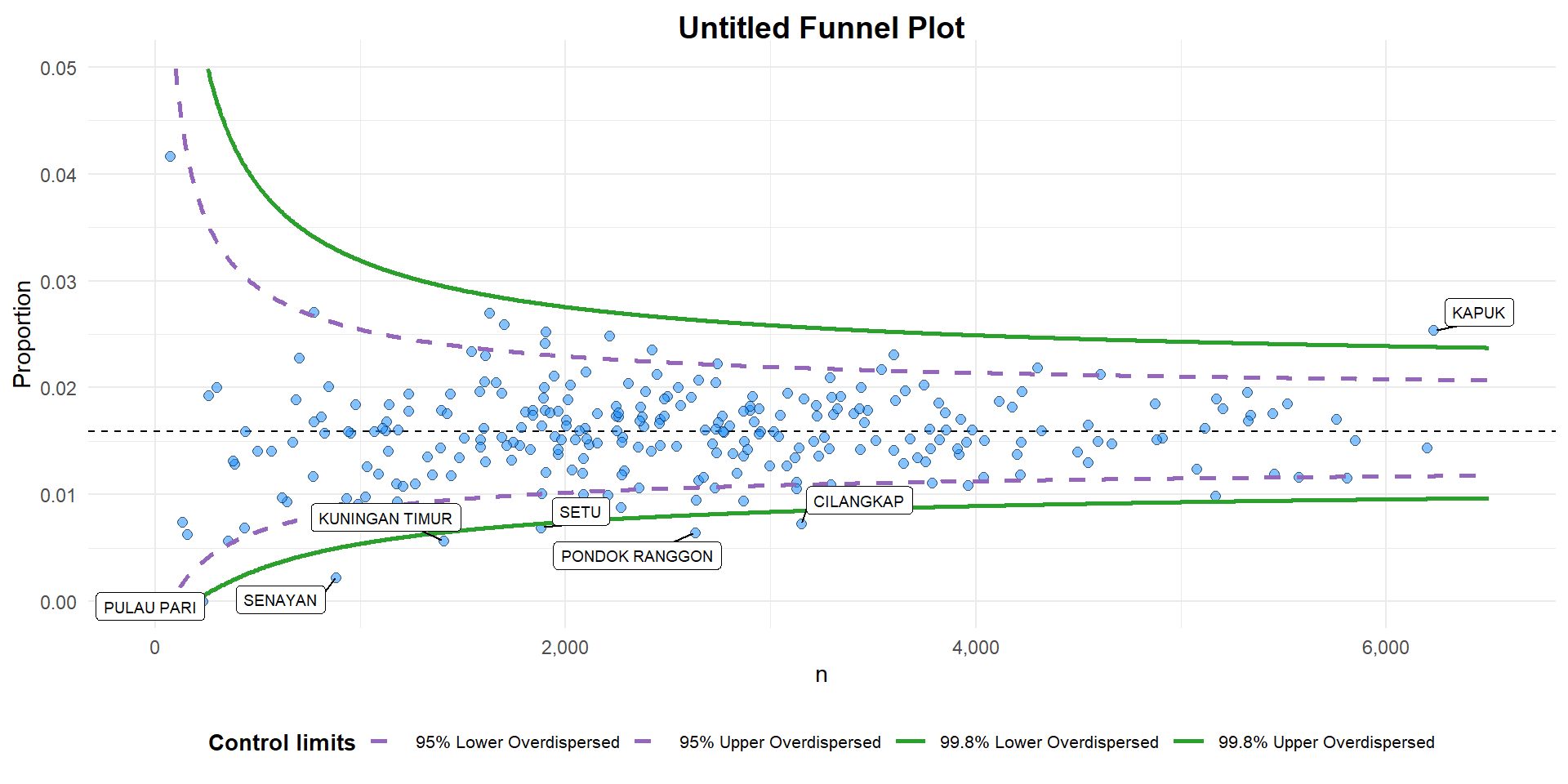
A funnel plot object with 267 points of which 7 are outliers.
Plot is adjusted for overdispersion. data_typeargument is used to change from default “SR” to “PR” (i.e. proportions)xrangeandyrangeare used to set the range of x-axis and y-axis
2.3 Makeover 2
The code chunk below plots a funnel plot.
funnel_plot(
numerator = covid19$Death,
denominator = covid19$Positive,
group = covid19$`Sub-district`,
data_type = "PR",
xrange = c(0, 6500),
yrange = c(0, 0.05),
label = NA,
title = "Cumulative COVID-19 Fatality Rate by Cumulative Total Number of COVID-19 Positive Cases", #<<
x_label = "Cumulative COVID-19 Positive Cases", #<<
y_label = "Cumulative Fatality Rate" #<<
)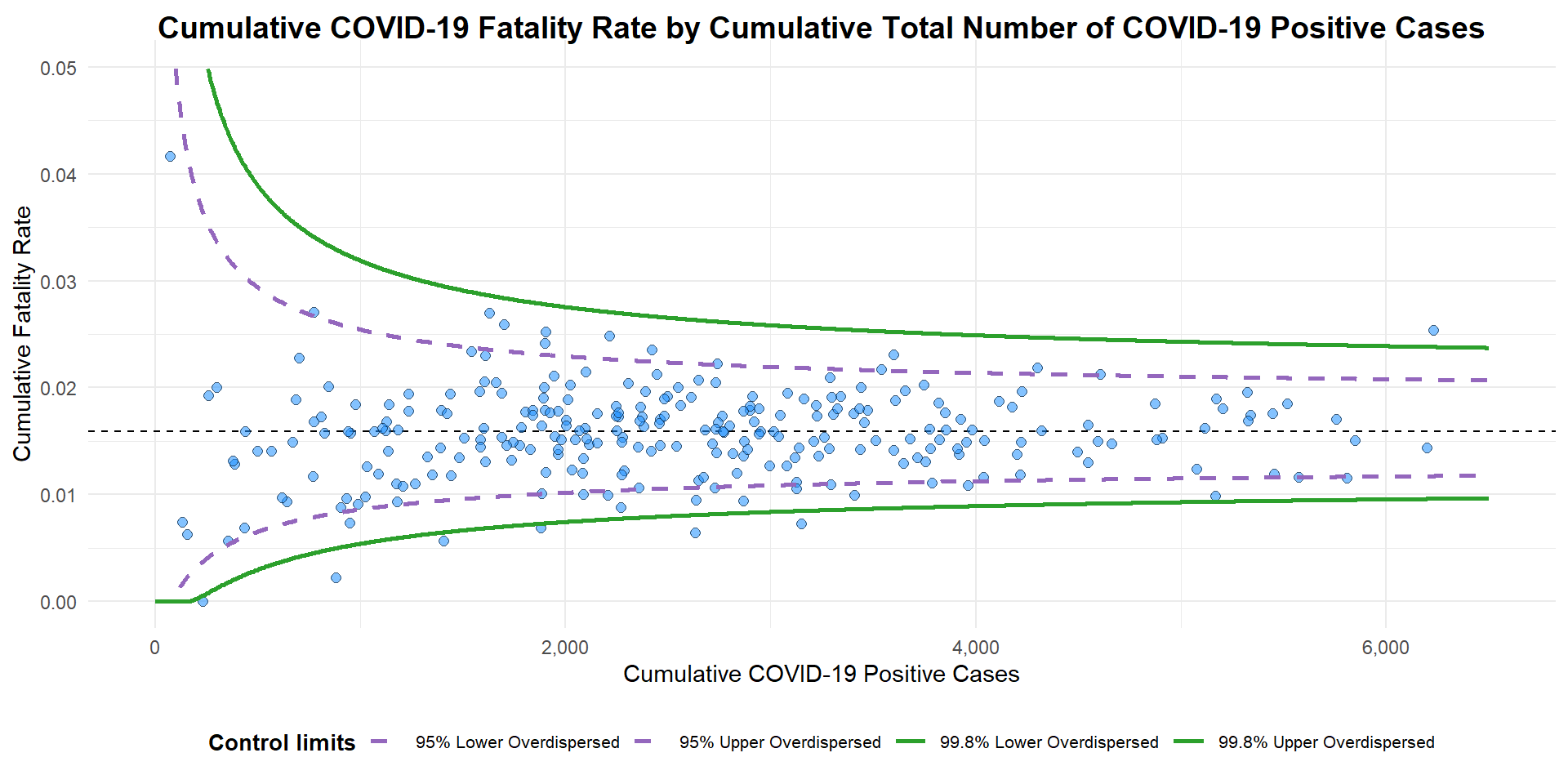
A funnel plot object with 267 points of which 7 are outliers.
Plot is adjusted for overdispersion. label = NAargument is to removed the default label outliers feature.titleargument is used to add plot title.x_labelandy_labelarguments are used to add/edit x-axis and y-axis titles.
3 Funnel Plot for Fair Visual Comparison: ggplot2 methods
In this section, you will gain hands-on experience on building funnel plots step-by-step by using ggplot2. It aims to enhance you working experience of ggplot2 to customize speciallized data visualization like funnel plot.
3.1 Computing the basic derived fields
To plot the funnel plot from scratch, we need to derive cumulative death rate and standard error of cumulative death rate.
df <- covid19 %>%
mutate(rate = Death / Positive) %>%
mutate(rate.se = sqrt((rate*(1-rate)) / (Positive))) %>%
filter(rate > 0)Next, the fit.mean is computed by using the code chunk below.
fit.mean <- weighted.mean(df$rate, 1/df$rate.se^2)3.2 Calculate lower and upper limits for 95% and 99.9% CI
The code chunk below is used to compute the lower and upper limits for 95% confidence interval.
number.seq <- seq(1, max(df$Positive), 1)
number.ll95 <- fit.mean - 1.96 * sqrt((fit.mean*(1-fit.mean)) / (number.seq))
number.ul95 <- fit.mean + 1.96 * sqrt((fit.mean*(1-fit.mean)) / (number.seq))
number.ll999 <- fit.mean - 3.29 * sqrt((fit.mean*(1-fit.mean)) / (number.seq))
number.ul999 <- fit.mean + 3.29 * sqrt((fit.mean*(1-fit.mean)) / (number.seq))
dfCI <- data.frame(number.ll95, number.ul95, number.ll999,
number.ul999, number.seq, fit.mean)3.3 Plotting a static funnel plot
In the code chunk below, ggplot2 functions are used to plot a static funnel plot.
Code
p <- ggplot(df, aes(x = Positive, y = rate)) +
geom_point(aes(label=`Sub-district`),
alpha=0.4) +
geom_line(data = dfCI,
aes(x = number.seq,
y = number.ll95),
size = 0.4,
colour = "grey40",
linetype = "dashed") +
geom_line(data = dfCI,
aes(x = number.seq,
y = number.ul95),
size = 0.4,
colour = "grey40",
linetype = "dashed") +
geom_line(data = dfCI,
aes(x = number.seq,
y = number.ll999),
size = 0.4,
colour = "grey40") +
geom_line(data = dfCI,
aes(x = number.seq,
y = number.ul999),
size = 0.4,
colour = "grey40") +
geom_hline(data = dfCI,
aes(yintercept = fit.mean),
size = 0.4,
colour = "grey40") +
coord_cartesian(ylim=c(0,0.05)) +
annotate("text", x = 1, y = -0.13, label = "95%", size = 3, colour = "grey40") +
annotate("text", x = 4.5, y = -0.18, label = "99%", size = 3, colour = "grey40") +
ggtitle("Cumulative Fatality Rate by Cumulative Number of COVID-19 Cases") +
xlab("Cumulative Number of COVID-19 Cases") +
ylab("Cumulative Fatality Rate") +
theme_light() +
theme(plot.title = element_text(size=12),
legend.position = c(0.91,0.85),
legend.title = element_text(size=7),
legend.text = element_text(size=7),
legend.background = element_rect(colour = "grey60", linetype = "dotted"),
legend.key.height = unit(0.3, "cm"))
p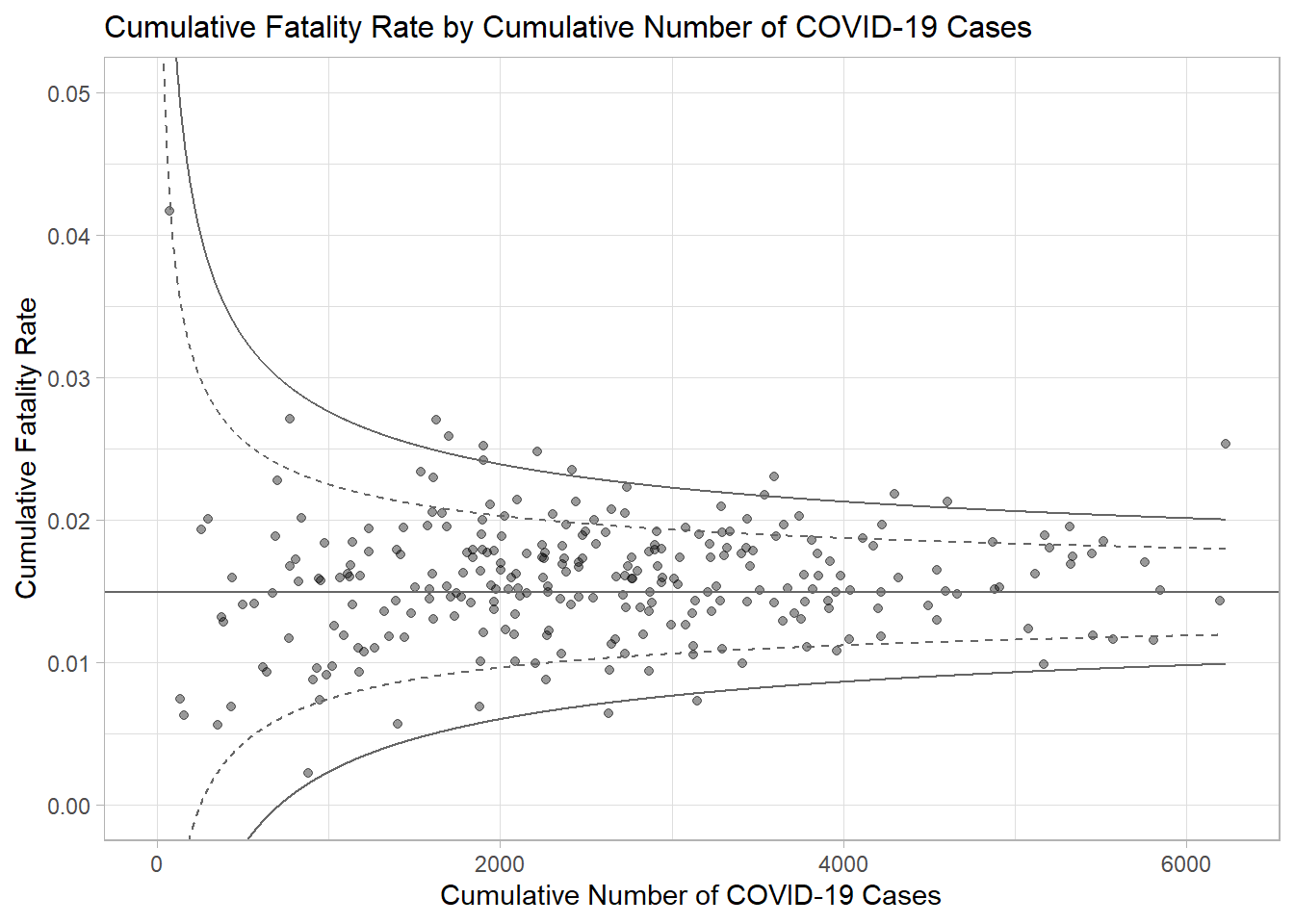
3.4 Interactive Funnel Plot: plotly + ggplot2
The funnel plot created using ggplot2 functions can be made interactive with ggplotly() of plotly r package.
fp_ggplotly <- ggplotly(p,
tooltip = c("label",
"x",
"y"))
fp_ggplotly